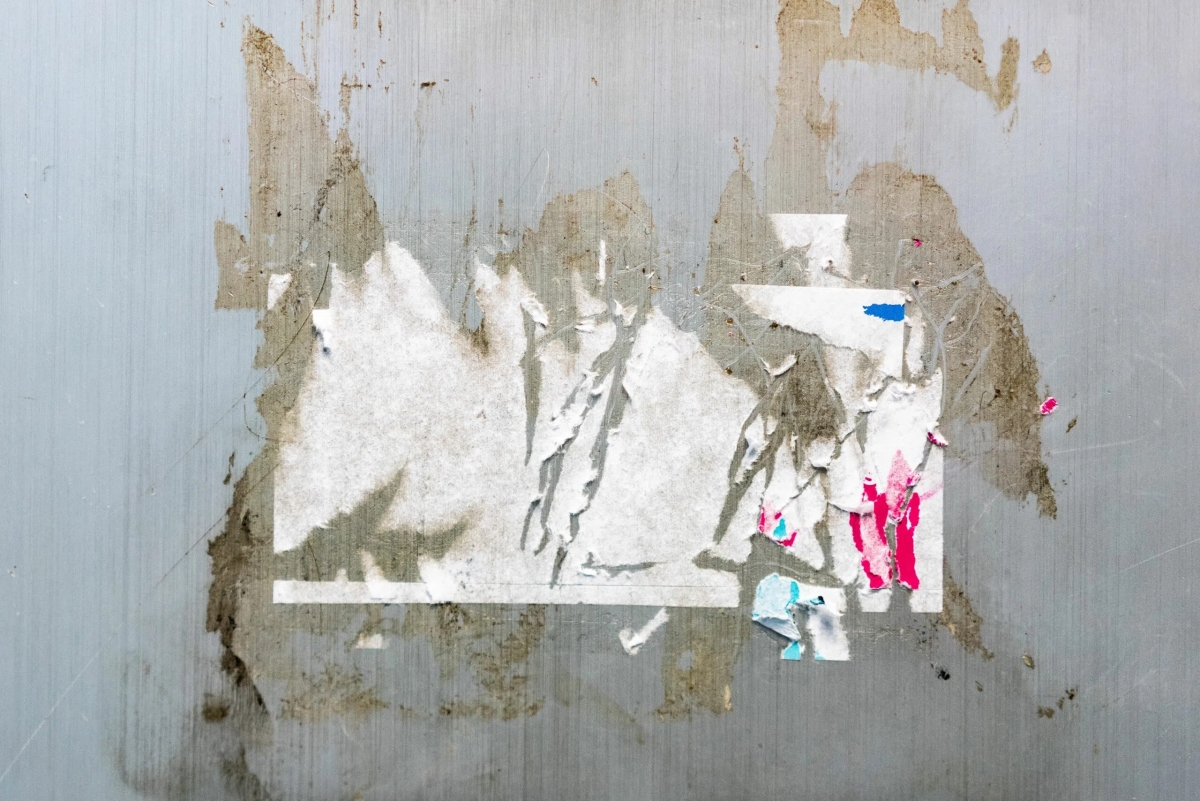
Residue can act as a contaminant
Residue is material that remains after cleaning, like grease left over on a frying pan. It can also be a liquid residue that’s left over at the bottom of a bottle, pot, or can, and even moisture remaining at the base of a sterilization container or tray after sterilization. When it comes to removal of moisture in a container or sterilized tray this is easy to fix. Use an adequate amount of dry time and containers like Case Medical’s SteriTite container made with thermal conductive aluminum. with a validated 5-to-8-minute minimal dry time. But when it comes to other residuals like sticky residue, like detergent gels or powders also tape adhesive that is another story.
What causes residue
The residue left behind after using cleaning products is typically caused by the ingredients in the cleaner not being fully removed or rinsed away. Some residues are free-rinsing and easy to remove, others are “sticky” and waxy and can be difficult to remove from the surface. Recently, The Joint Commission cited health care facilities for the presence of adhesive residue left on surgical devices, including containers and trays from labels used to identify the contents of a tray. One account reached out to us to purchase over 100 new instrument baskets as it was easier to replace than trying to pull back layers of sticky barcode labels.


Not all detergents are created equal
Reusable medical devices are intended to be cleaned, disinfected, and/or terminally sterilized before subsequent patient use. Improper cleaning, rinsing, and drying can lead to health care acquired infections. The residual contaminants can interfere with subsequent sterilization and disinfection. Detergent-based formulations play an important role in the effectiveness of clinical soil (like blood, fat, tissue, mucus) removal from a device. Manufacturers are responsible for demonstrating the safety of cleaning formulations when they are used for medical device reprocesing. Nonetheless, many contain hazardous chemical ingredients that become even more of a risk when devices are not properly rinsed or when devices are cleaned in cart washers with recycled wash water, gaining an extra dose of cleaning agent each time the wash water is re- used.
Validating instrument chemistries is a voluntary process
It is up to the individual detergent manufacturer to validate or certify that their instrument cleaners are safe to use and effective. Most don’t validate and certainly not certify. According to an article in AAMI news, “It has long been understood that the manufacturers of cleaning formulations are responsible for demonstrating the inherent risks that come with the intended use of their product. However, according to a team of concerned scientists, lab operations managers, and microbiological quality and sterility assurance specialists, there are no regulations that specify how manufacturers can help users determine the risk of residual chemicals on device surfaces after cleaning.”


Case Medical not only validates but certifies, too
Case Medical is a 6-time U.S. EPA Safer Choice Partner of the Year, most recently for 2023. We ensure that our products are safe and effective. We have had a partnership with the U.S. Environmental Prevention Agency since 2011 and proudly display the Safer Choice label on our cleaning solutions. Last year, we were awarded the label for our Case Care Skin Cleanser and most recently obtained certification for our newly formulated CSR Ink and Adhesive Remover. At Case Medical, we believe in continuous improvement and expanding our sustainable, certified products originally designed for health care applications to the community at large.
Visit us anytime at www.casemed.com to learn more about our products and services. We are here to help.
Kindest Regards,